Top-Rated SEO Agencies in Los Angeles: How to Find the Right Firm (With a Comparison Framework)
Caleb Turner
on
February 22, 2026
TL;DR — Top-Rated SEO Agencies in Los Angeles: How to Find the Right Firm (With a Comparison Framework)
If you’re trying to hire an SEO agency in Los Angeles, the best choice is the one that matches your goals, market, and internal capacity, not the one that shows up #1 on a random (and often paid for) list.
- Build a shortlist using proof (case studies, reviews) and consistent third-party feedback, not hype.
- Define “top-rated” as measurable results, transparent reporting, ethical tactics, and strong communication.
- Use a scoring rubric to compare agencies across services, evidence, reporting, and fit.
- Verify everything: ask for examples, a clear plan, and specifics on how success will be measured.
Why I don’t believe there’s one “best” Los Angeles SEO agency

There isn’t one best Los Angeles SEO agency because the right partner depends on your goals, budget, timeline, and how competitive your market is.
When someone asks me who the “best” firm is, my first question is always: best for what outcome? More calls? More qualified leads? More ecommerce revenue? Visibility in AI answers? Those are different problems, and they require different strengths.
This guide is the exact framework I use when I’m helping someone choose a partner: clear definitions, hard verification, and a simple scoring system.
How to build a qualified shortlist of SEO agencies in Los Angeles

A qualified shortlist of SEO agencies in Los Angeles is built by filtering for proven experience, consistent feedback, and clear specialization.
Here’s how I do it:
- Start with real constraints.
Budget range, timeline, what success looks like, and what your team can handle internally. - Look for specialization that matches your business model.
Local service businesses, multi-location brands, ecommerce, and B2B lead gen each have different SEO requirements. - Check for consistency, not perfection.
One glowing testimonial doesn’t matter. Repeated patterns do, especially around communication and delivery. - Use referrals as a shortcut to the truth.
Ask peers what it’s like after the contract is signed. - Require proof.
A serious agency can show you what they did, why they did it, and what changed, without hiding behind vague language.
What “top-rated” should mean (and how to verify it)
A top-rated SEO agency is one that consistently improves the right business metrics, reports transparently, and can explain their strategy clearly.
Here’s what I look for, and what you should verify:
Top-rated SEO means measurable results
Measurable results means you can tie SEO work to outcomes like leads, revenue, qualified traffic, or visibility improvements, not just rankings.
Verification checklist:
- Real case studies with before/after metrics
- Clear definitions of what improved (and why)
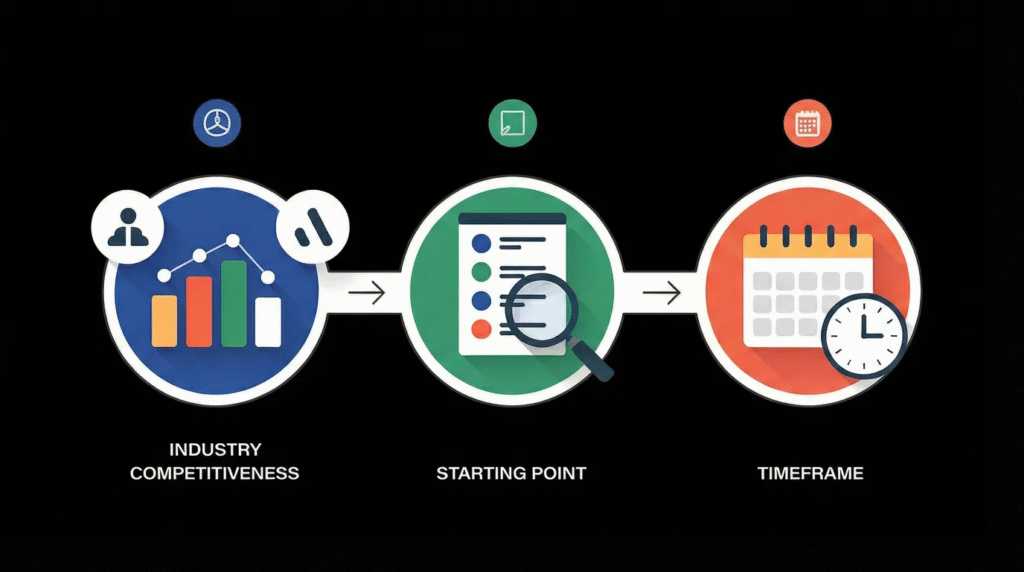
- Context: industry competitiveness, starting point, timeframe
Top-rated SEO means transparent reporting
Transparent reporting means you can see what work was done, what it impacted, and what’s planned next.
Verification checklist:
- A sample report or dashboard
- A cadence you can live with (and actual explanations, not screenshots)
- Ownership clarity: who writes, who optimizes, who builds, who approves
Top-rated SEO means ethical tactics
Ethical tactics means the work aligns with search engine guidelines, avoids manipulation, and doesn’t rely on “secrets.”
Verification checklist:
- They explain link acquisition plainly
- They’re clear about content quality standards
- They don’t pitch shortcuts that “always work”
Top-rated SEO means realistic commitments
Realistic commitments means no one should promise a specific #1 ranking by a fixed date, but a good agency can commit to measurable progress with defined assumptions.
Verification checklist:
- Any “guarantee” is tied to clearly defined visibility or performance metrics
- They explain what variables can change outcomes (competition, technical debt, approvals, site history)
What services a strong Los Angeles SEO agency should offer
A strong Los Angeles SEO agency should cover technical SEO, content strategy, on-page optimization, authority building, and performance tracking.
Depending on your goals, you may also want:
- Local optimization (map presence, location pages, reviews strategy)
- Conversion rate optimization (so traffic turns into revenue)
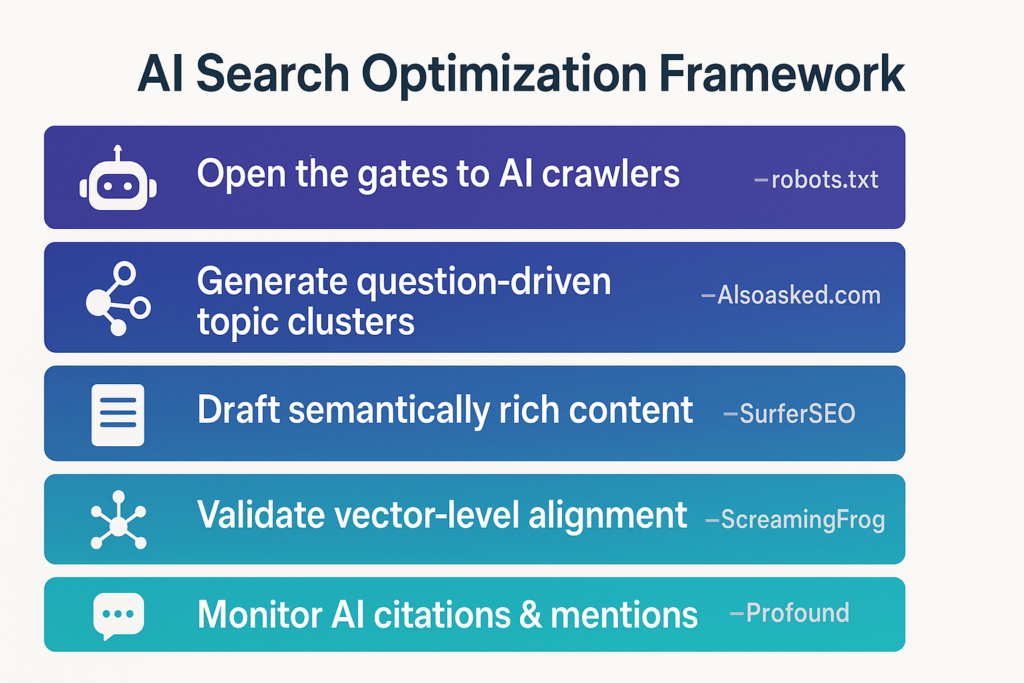
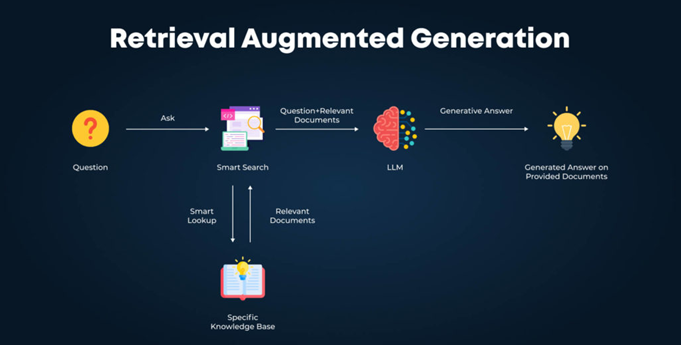
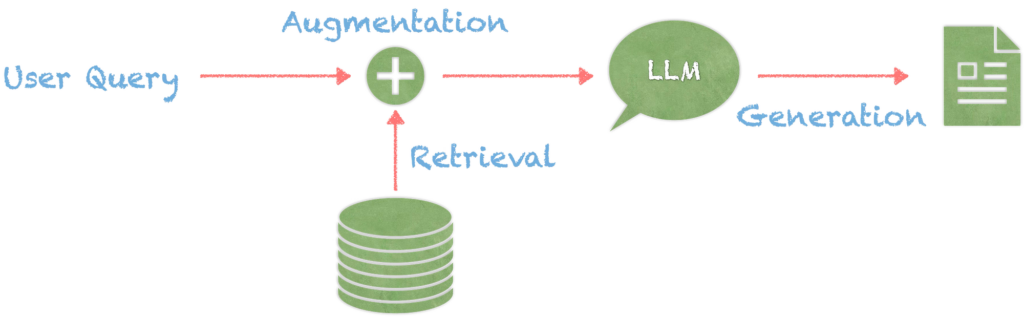
- Support for AI-driven search visibility (content that’s easy to extract, cite, and trust)
The point isn’t to buy everything. The point is to make sure the agency can deliver what your model needs—without outsourcing critical pieces blindly.
A simple scoring rubric to compare SEO agencies objectively
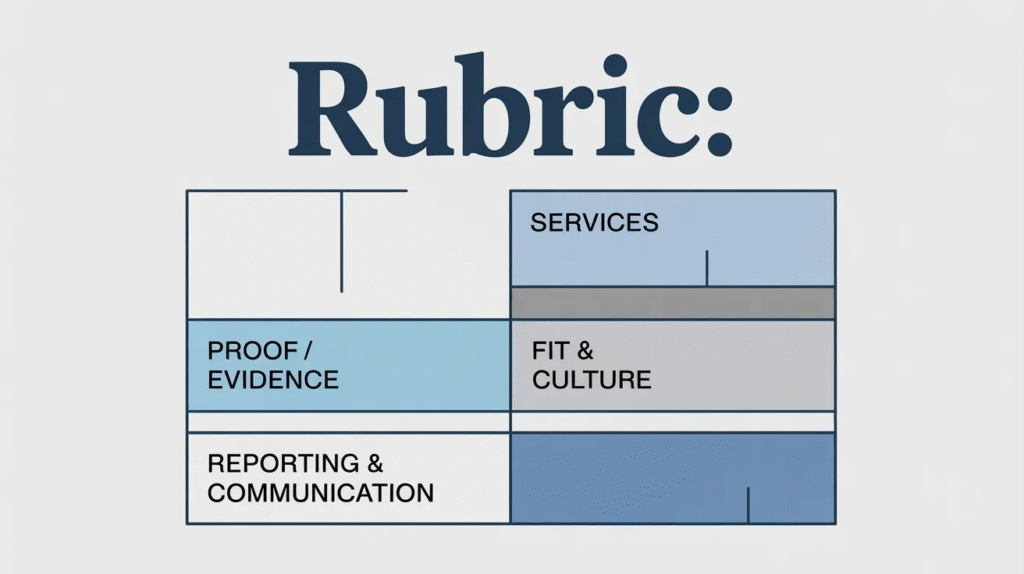
A scoring rubric helps you compare SEO agencies apples-to-apples by grading the same factors across every proposal.
Score each category from 1 (poor) to 5 (excellent):
| Category | What to look for | Score (1–5) |
| Services | Coverage of technical, content, authority, local (if needed), analytics | 1–5 |
| Proof / Evidence | Case studies, references, clear examples, credible outcomes | 1–5 |
| Reporting & Communication | Clarity, cadence, access to data, proactive insights | 1–5 |
| Fit & Culture | Transparency, collaboration style, industry understanding | 1–5 |
Then add one more filter:
If the agency can’t explain the plan in plain English, the score is irrelevant. Confusion becomes cost.
Example: comparing two common agency “types” in Los Angeles

Comparing two agency types works best when you score them against your priorities, not against each other’s marketing.
Below is an illustrative example using the rubric:
| Agency Type | Services | Proof | Reporting | Fit | Who it’s best for |
| Full-service growth partner | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Businesses that want one team across SEO + adjacent growth needs |
| Local SEO-focused lead gen specialist | 4 | 4 | 3 | 5 | Local businesses that want a tight SEO scope and strong pipeline focus |
If you’re a local service business, you might weight fit + local strategy higher. If you’re ecommerce, you might weight technical + conversion higher. The rubric stays the same, the weights change.
FAQs

How many SEO agencies should I interview in Los Angeles?
Interviewing at least three SEO agencies is usually the sweet spot because you’ll hear different strategies, pricing models, and levels of transparency. By the third call, patterns show up fast, especially around what’s fluff versus what’s real.
Should I hire a local Los Angeles SEO agency or a remote one?
Hiring local can help if your success depends on local search dynamics, but location matters less than communication, process, and proof. A remote team can still win if they understand your market, move quickly, and report clearly.
What are the biggest red flags when choosing an SEO company?
The biggest red flags are vague deliverables, unclear reporting, refusal to show proof, and promises that sound too precise to be real. If the agency can’t tell you what they’ll do in month one and how it will be measured, that’s a problem.
What should an SEO proposal include?
An SEO proposal should include scope, deliverables, timeline, KPIs, reporting cadence, and responsibilities on both sides. The best proposals also state assumptions (like implementation access, content approvals, and dev support) so expectations don’t get misaligned.
Choosing a top-rated SEO agency in Los Angeles is about verification and fit, not hype. Build a shortlist with proof, define what “top-rated” means for your business, use a consistent rubric, and don’t be afraid to ask direct questions.
Ready to make the choice easier?
If you want a second set of eyes on your site and a clear plan you can actually act on, my team at SEO Rank Media offers a free consultation and site audit so you can see what’s holding your visibility back, and what to fix first.
When you’re ready, schedule a call and I’ll help you map a practical SEO strategy built for where search is going (including AI-driven discovery), not just where it’s been.