The New State of Search in 2025 and Beyond: Optimizing for AI Mode and LLM Discovery
If you’ve felt whiplash from Google’s nonstop updates: AI Overviews, generative snippets, and now the full rollout of AI Mode into core results, you’re not imagining it. Search is undergoing its most radical transformation since the birth of PageRank. And the implications extend far beyond Google. In a world where LLMs like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude are actively retrieving, reasoning, and rewriting content, visibility is no longer measured in blue links.
In this guide, you’ll understand how AI Mode works under the hood, what Google recommends explicitly (and what it doesn’t say out loud), and how to structure your content for retrieval augmented generation(RAG), across Google and the new class of LLM-native search engines.
1. From “Ten Blue Links” to a Web of AI Summaries
For decades, SEO meant chasing organic rankings. But in 2025, users expect a different experience: conversational, multimodal, and personalized. Google’s AI Mode, which rolled out U.S.-wide on May 20, 2025, doesn’t just augment results, it replaces traditional listings with AI-generated summaries that quote from multiple sources simultaneously.
This is not a Google-only story. Platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini also synthesize content from across the web, using similar pipelines: chunking, embedding, retrieval, reranking, and LLM generation. Your content might be cited without ever earning a click, or worse, it may not be retrieved at all if it’s not semantically aligned.
AI Mode’s secret weapon is deep personalization: Google fuses data from Gmail, Calendar, Chrome, Maps, and YouTube to tailor summaries. The shift is clear: we’ve moved from “optimize for keywords” to “optimize for meaning.”
2. Google’s AI Mode: The Stack That Writes the Answers
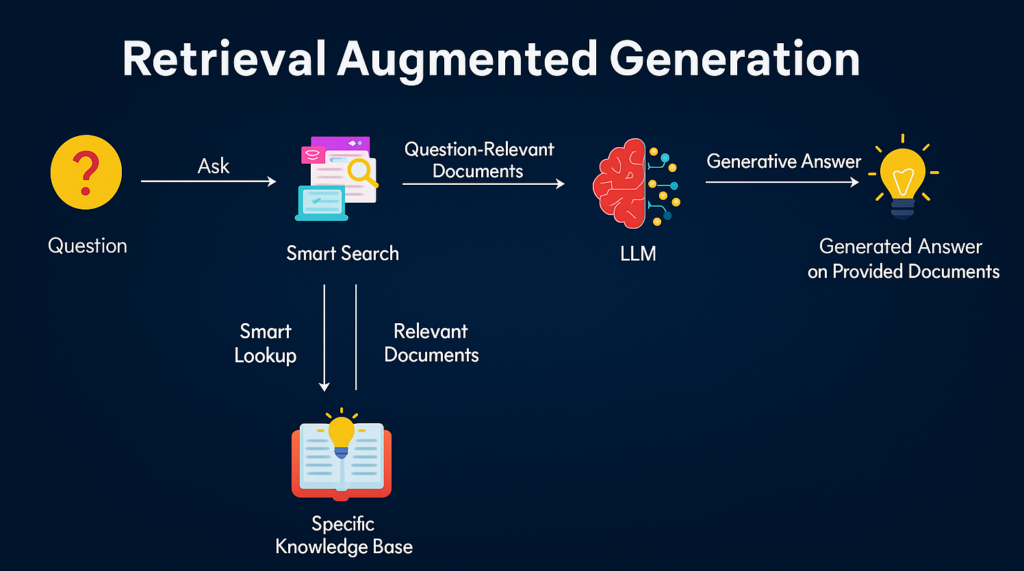
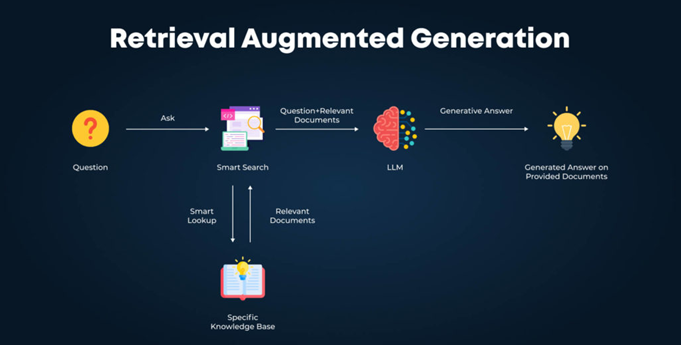
To demystify how your content is selected and quoted in AI Mode, here’s a breakdown of Google’s layered system, most of which is mirrored by other LLMs and is what RAG consists of:
| Layer | Role | How it Works |
| BERT / T5 | Linguistic interpreters | Translate queries to understand intent and direction. |
| Vector Embeddings | Semantic mapmakers | Place ideas in conceptual space; “jaguar” the car ≠ “jaguar” the animal. |
| ScaNN Retrieval | Ultra-fast content locators | Fetch the most semantically relevant chunks in milliseconds. |
| Hybrid Rerankers | Rational judges | Combine keyword scores and semantic scores; pick the most coherent passage. |
| Gemini Flash/Pro | Creative summarizers | Compose a humanlike response from many retrieved sources. |
Google, OpenAI, and Perplexity all use a variation of this stack. The question is no longer, “Is my page ranking?”. It’s, “Is my content retrievable, relevant, and reusable in an AI summary?”
3. The AI Optimization Imperative: What Google (and Others) Recommend
Google’s own blueprint, published May 21, 2025, provides clarity, but with nuance. These principles aren’t just best practices for Google—they apply to any LLM-powered platform that retrieves and assembles answers.
✅ Do:
- Create original, human-centric content – Generic rewrites vanish from summaries. Depth wins.
- Ensure crawlability – Don’t accidentally block Google-Extended, GeminiBot, or GPTBot.
- Optimize structure for readability – Use headings, schema, and direct answers.
- Include rich media – Images and videos can appear in multimodal answers.
- Use preview controls wisely – Overrestrictive snippet settings can remove you entirely.
- Verify your structured data – If it misaligns with visible content, it may be ignored or penalized.
❌ Don’t:
- Chase AI placement hacks – Prompt templates change daily.
- Stuff with synonyms – Semantic distance matters more than density.
- Block LLMs for “content protection” – You’ll be excluded from the answer graph.
Note: Traditional SERPs and classic SEO are not obsolete—but they are rapidly shrinking in importance. Many users will still browse organic results, especially for transactional queries. However, AI-generated responses, smart assistants, and multimodal summaries are becoming the default interface for information retrieval. SERPs now represent just one channel among many in the optimization landscape.
4. An AI-First Optimization Framework
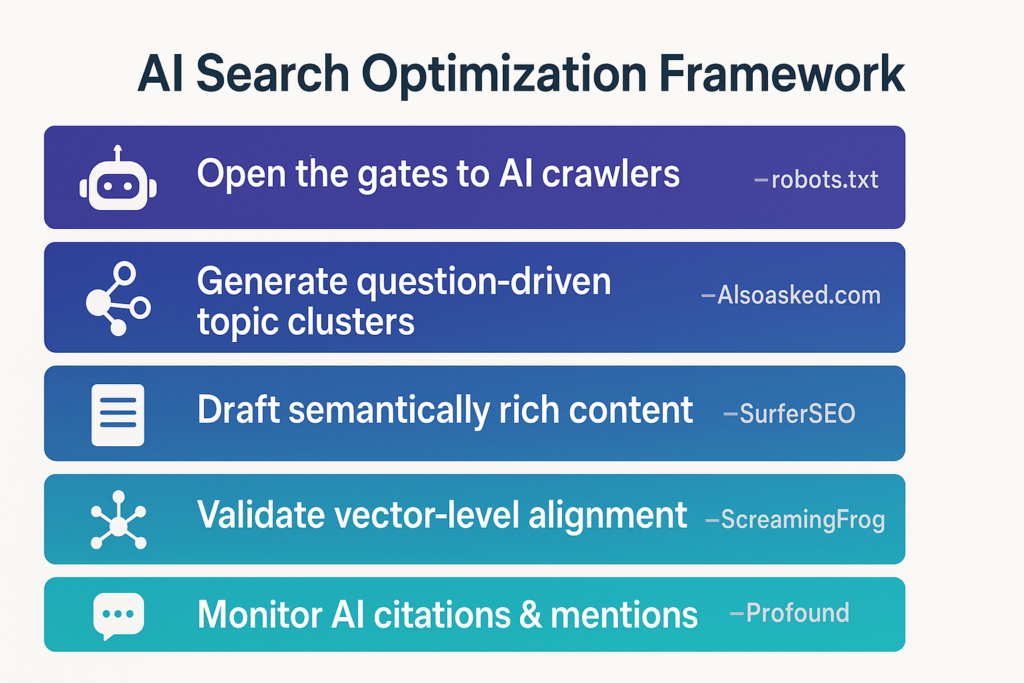
Below is the exact workflow our agency uses when auditing sites for AI Mode and LLM optimization. We’ve even specified tools that you can use at each stage purely for the education of the reader. This is not an endorsement and we have no affiliation with any of these brands:
Open the gates to AI crawlers
- Audit robots.txt and server logs for Google-Extended, Google-LLM, GeminiBot, and GPTBot.
- Remove legacy disallow rules on JS, CSS, or /api/ endpoints; AI models fetch full render trees.
→ Tool: logflare.app, openai.com/gptbot
Generate question-driven topic clusters to mimic “Query Fan-Out”
- De-duplicate and cluster by user intent (how, why, cost, vs).
- Prioritize clusters based on traffic opportunity and business value.
→ Tool: alsoasked.com
Draft semantically rich content
- Begin each section with a concise 1–2 sentence direct answer (<80 words).
- Support with original research, media, expert commentary.
- Use H2/H3 subheads as natural language questions.
→ Tool: surferseo.com
Validate vector-level alignment
- Embed draft paragraphs using OpenAI or TensorFlow.
- Compute cosine similarity between your content and target queries.
- Iterate until ≥ 0.85 similarity is achieved.
→ Tool: Screaming Frog SEO Spider v22.0
Monitor AI citations & mentions
- Track when your URL appears in Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, ChatGPT, etc.
- Set alerts for declines; rework and refresh passages accordingly.
→ Tool: tryprofound.com
5. Case Study Snapshot: A Cross-LLM Win
A health brand published an article titled “Are stainless steel bottles safe during pregnancy?” using this methodology:
- Opened with a 70-word evidence-based answer.
- Embedded lab-test data (image) and a 45-second expert video.
- Verified 0.91 cosine similarity with key intent queries.
- Appeared in Google AI Mode, Perplexity responses, and ChatGPT citations.
- Result: 28% increase in time-on-site and a 17% higher cart-to-visit rate from AI referrals.
6. FAQ: What This Means for SEO
Is SEO dead?
No—but it’s evolving. Optimization now includes vector alignment, retrievability, and AI authority.
Do I need new pages just for AI Mode?
Not at all. Structuring your existing content with questions and direct answers serves both AI and human audiences.
What metrics matter now?
Track AI citations, retrieval frequency, and embedding scores. Legacy KPIs like CTR and bounce rate are secondary in zero-click environments.
7. Action Checklist (Print This)
✅ Allow GPTBot, GeminiBot, Google-Extended
✅ Refresh content clusters quarterly
✅ Lead each H2 with a sub-100-word answer
✅ Verify cosine similarity ≥ 0.85
✅ Track citations across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google
✅ Validate structured data and crawlability
✅ Optimize for conversions and engagement—not vanity metrics
8. Final Thoughts
The AI era isn’t on the horizon, it’s here. AI Mode is becoming the standard lens for Google Search, and LLM-native discovery platforms are competing directly for user attention. Success now means thinking like a retrieval engine, not just a rank chaser.
Ready to thrive in this new landscape? Start with our AI Optimization Checklist, then audit your five highest-traffic pages using LLM-aware tools.
The future of search rewards those who are findable, quotable, and semantically aligned.