What the 2025 GEO Study Reveals About Ranking in AI Answers (and How I Apply It)
Caleb Turner
on
January 27, 2026
TL;DR
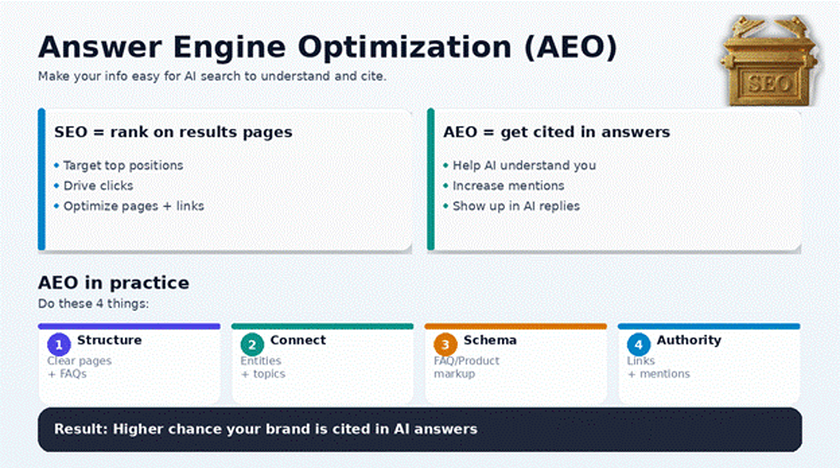
A 2025 research study from researchers at MIT and Columbia University tested what actually moves content up in AI-generated rankings. Their big finding wasn’t “use this one weird prompt.” It was that repeatable, reliable gains come from a consistent structure: match user intent, stay factual, show clear differentiation, use evidence, and format content so it’s easy to extract.
I built a custom internal tool inspired by that study to help me (and my clients) turn messy, long-form information into “AI-ready” answer blocks that are more likely to be pulled and preferred in AI results. We’re actively expanding that tool to make it more comprehensive, and it’s already being used to guide client content.
I’ve spent the last couple of years watching the same pattern play out across industries:
- Some brands get mentioned in AI answers… but show up as the third or fourth recommendation.
- Others get pulled sometimes… but inconsistently.
- And a few dominate because their content is the easiest to trust, quote, and rank.
That’s why I pay attention when researchers publish something that goes beyond opinions and actually tests what works.
The research team from MIT and Columbia University ran the study (E-GEO: A Testbed for Generative Engine Optimization in E-Commerce) to measure how answer engine rankings change based on how content is written. They used thousands of real-world shopping-style queries, rewrote product descriptions using different approaches, and tracked whether the rewritten versions moved up or down in AI rankings.
What I’m sharing below is the practical version of what matters, and how you can apply it whether you sell products or services.
The two-step reality: getting pulled vs getting preferred
Most brands only think about one part of the problem.
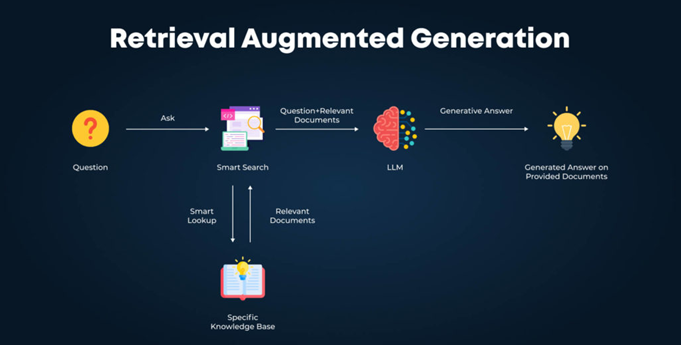
Step 1: Retrieval (getting pulled in)
This is whether your page, brand, or product even gets included as a possible answer.
Step 2: Re-ranking (getting preferred)
This is where the AI decides what’s “best,” “second best,” and so on.
The 2025 study focused heavily on that second step: once options are in the set, what makes one rise to the top?
If you’re investing in content for AI visibility, you want both:
● content that reliably gets pulled
● content that reliably gets ranked as the preferred option
What the researchers actually did (in plain English)
Here’s the simple version of the test:
- They took 7,000+ real “what should I buy?” style posts from Reddit.
- They matched each query to the 10 most relevant Amazon product listings using a semantic similarity method (basically, “meaning match,” not just keyword match).
- They rewrote product descriptions using different prompt styles.
- They measured whether the rewritten descriptions moved up in the AI’s ranking.
- They then used a second model to iteratively improve the rewrite prompts until the rewrites performed better.
The purpose wasn’t to find a trick. It was to find patterns that hold up repeatedly across many queries and products.
That’s exactly what brands need right now, repeatable rules, not hype.
The most important practical takeaway
AI rankings reward content that makes it easy to confidently choose and easy to quote.
That’s why the winning patterns consistently included:
1) Clear intent match
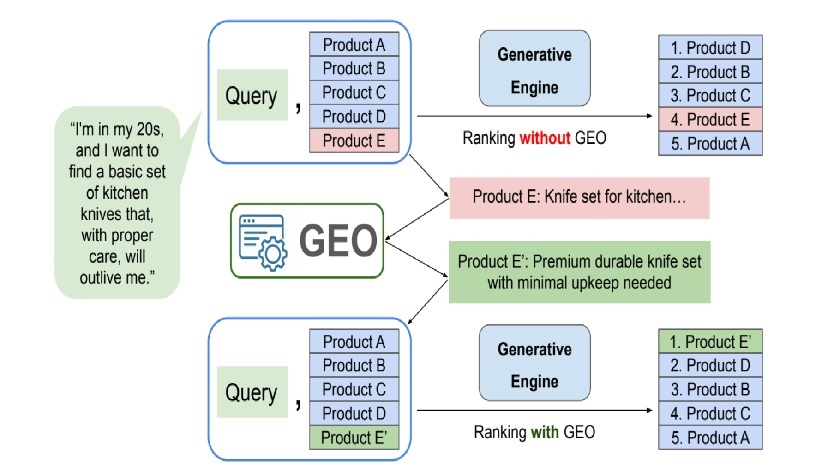
The best performing rewrites aligned tightly with what the user actually asked for, especially long, conversational queries with constraints.
Not “Knife set for kitchen.”
More like:
“Premium durable knife set with minimal upkeep needed.”
That shift matters because it directly mirrors the user’s real goal.
2) Factual grounding
One of the most consistent themes was factuality. Keep claims accurate, avoid embellishment, and preserve what can be supported.
In real life, that means:
● don’t guess
● don’t inflate benefits
● don’t claim “best” without support
3) Clear differentiation (your “why us” without fluff)
Competitive positioning mattered, especially when it was expressed as concrete differences, not generic marketing language.
Examples:
● materials, specs, certifications
● what’s included vs not included
● warranty terms
● durability, maintenance requirements
● constraints the product/service is best for (and not best for)
4) Evidence signals
When you can back something up with data or reputable references, do it. Evidence helps the AI system “trust” the content and reuse it.
For service businesses, evidence can be:
● licensing and certifications
● documented process steps
● before/after metrics
● review volume and rating
● pricing ranges and what drives them
5) Scannable formatting
This one is huge, and it matches what I’ve seen in the wild. Content that’s easy to scan is easier for AI systems to lift into answers.
Headings, bullets, short blocks, ranges, and direct definitions beat long paragraphs every time.
What didn’t work as well

A lot of “internet advice” about AI visibility leans into tone or style:
● “Write like an ad”
● “Be super persuasive”
● “Tell a story”
● “Sound authoritative”
The study showed that these approaches can be inconsistent, and in some cases can even hurt performance if they reduce factual clarity or drift away from the user’s intent.
The takeaway: style is secondary; structure and usefulness come first.
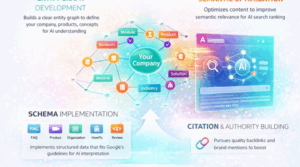
The custom tool I built (inspired by the study)

This study didn’t just confirm what I suspected, it gave me a structure I could build around.
So I built an internal GPT-powered re-ranking workflow inspired by the study’s re-ranking logic.
Here’s what it does in practical terms:
What my tool does today
- I feed it a target query (example: “How much does carpet cleaning cost in Northern Virginia?”).
- It ingests multiple content “chunks” pulled from top-performing pages on Google.
- It ranks those chunks based on which one most directly and completely answers the query.
- It rewrites the best chunk into multiple output formats, especially:
○ a tight “answer block”
○ a highly scannable version with headings and bullets
- It re-ranks the outputs and recommends the version most likely to be extractable and preferred in AI answers.
In short, it helps us consistently produce content that is accurate, aligned with intent, and formatted for extraction, which is exactly what the study suggests is repeatably effective.
How we’re expanding it
Right now we’re expanding the workflow to be more iterative, and mathematical about which content is most optimized. This will result in:
● content that more accurately reflects what AI engines reward
● stronger evidence handling
● consistency checks
● broader content formats
How we’re using it for clients
We’re already using this tool in our client work to:
● upgrade existing pages into AI-ready “answer-first” structures
● produce scannable sections that AI engines can quote cleanly
● reduce fluff while increasing proof and clarity
● align content with how people actually ask questions in AI tools
This is one of the ways we’ve been able to move faster while staying grounded and factual, because the tool forces discipline around intent, structure, and evidence.
Final thoughts

The 2025 MIT + Columbia E-GEO study supports something I’ve been emphasizing for a while:
If you want to rank well in AI answers, your content has to do more than “sound good.” It has to be the clearest match to the user’s intent, backed by facts, and formatted in a way that’s easy to extract and trust.
That’s why I built a tool around this, and why we’re expanding it and using it actively in client content.
If you want your site to show up more often and be preferred in AI answers, request my free AI visibility checklist. I’ll review your site and tell you:
● what’s preventing AI engines from pulling your pages
● what’s keeping you from being ranked as the “top” recommendation
● which pages to fix first for the fastest impact
You can implement the changes yourself, or my team at SEO Rank Media can handle it for you.